
Money laundering through online gambling
Despite strict regulations and heightened due diligence, online gambling remains a lucrative avenue for illicit actors seeking to launder money. In fact, gambling emerged as one of the top three sectors that incurred the highest amount of anti-money laundering (AML) fines in 2023 – racking up over $475 million in penalties.
While traditional casinos can provide criminals with an avenue to convert physical “dirty” cash into casino chips, online gambling presents different types of money laundering risks due to increased levels of anonymity. This article details the financial red flags compliance staff should be aware of, alongside best practices for mitigating these risks.
Money laundering risks in online gambling
Recognizing red flag behaviors and activities in online gambling transactions is essential for firms to mitigate financial crime risks effectively. By understanding these indicators, firms can fine-tune their systems to align with their risk appetite and address the challenges online gambling poses within their industry and jurisdiction. Some key money laundering risks in online gambling include:
- Anonymity: One of the primary risks associated with online gambling is the anonymity it affords users. Unlike traditional casinos that require face-to-face interactions, online platforms allow users to gamble with minimal personal information. Criminals exploit this by using stolen credit cards, fake identities, or cryptocurrencies to place bets and withdraw their “winnings,” effectively laundering their illegally obtained money.
- Multiple accounts and cross-border transactions: Online gambling sites often permit the creation of multiple accounts, which criminals can use to transfer money between accounts to obfuscate the origin of the funds. Additionally, the global nature of online gambling allows for cross-border transactions, further complicating efforts to trace illicit funds. These features make it difficult for regulators and financial institutions (FIs) to effectively track and prevent money laundering activities.
- The free flow of funds: Much like traditional casinos, where money flows freely and transactions are numerous, online gambling platforms facilitate the movement of large sums of money. This environment makes it easier for criminals to integrate their dirty money into the legitimate financial system. By placing bets and withdrawing winnings, they can make it appear as though their funds come from legitimate gambling activities.
- Regulatory challenges: The regulation of online gambling varies widely across different jurisdictions, creating challenges for authorities attempting to combat money laundering. Some countries have stringent regulations and robust monitoring systems (e.g., China), while others have more relaxed approaches (e.g., Malta). This inconsistency can create loopholes that criminals exploit to launder money through online gambling platforms.
Money laundering schemes in online gambling
Bad actors can exploit online gambling platforms at each of the three stages of money laundering:
- Placement: Illicit funds are introduced into the financial system by depositing money into gambling accounts using methods such as credit/debit cards, cryptocurrencies, prepaid cards, and checks.
- Layering: The source of the funds (SoF) is disguised through complex transactions involving multiple bets, transfers, and withdrawals within the gambling platform, making it difficult to trace the money’s origin.
- Integration: The laundered funds are withdrawn or used for legitimate transactions, which can include purchasing assets or transferring money to other accounts, effectively merging illicit funds with legitimate ones.
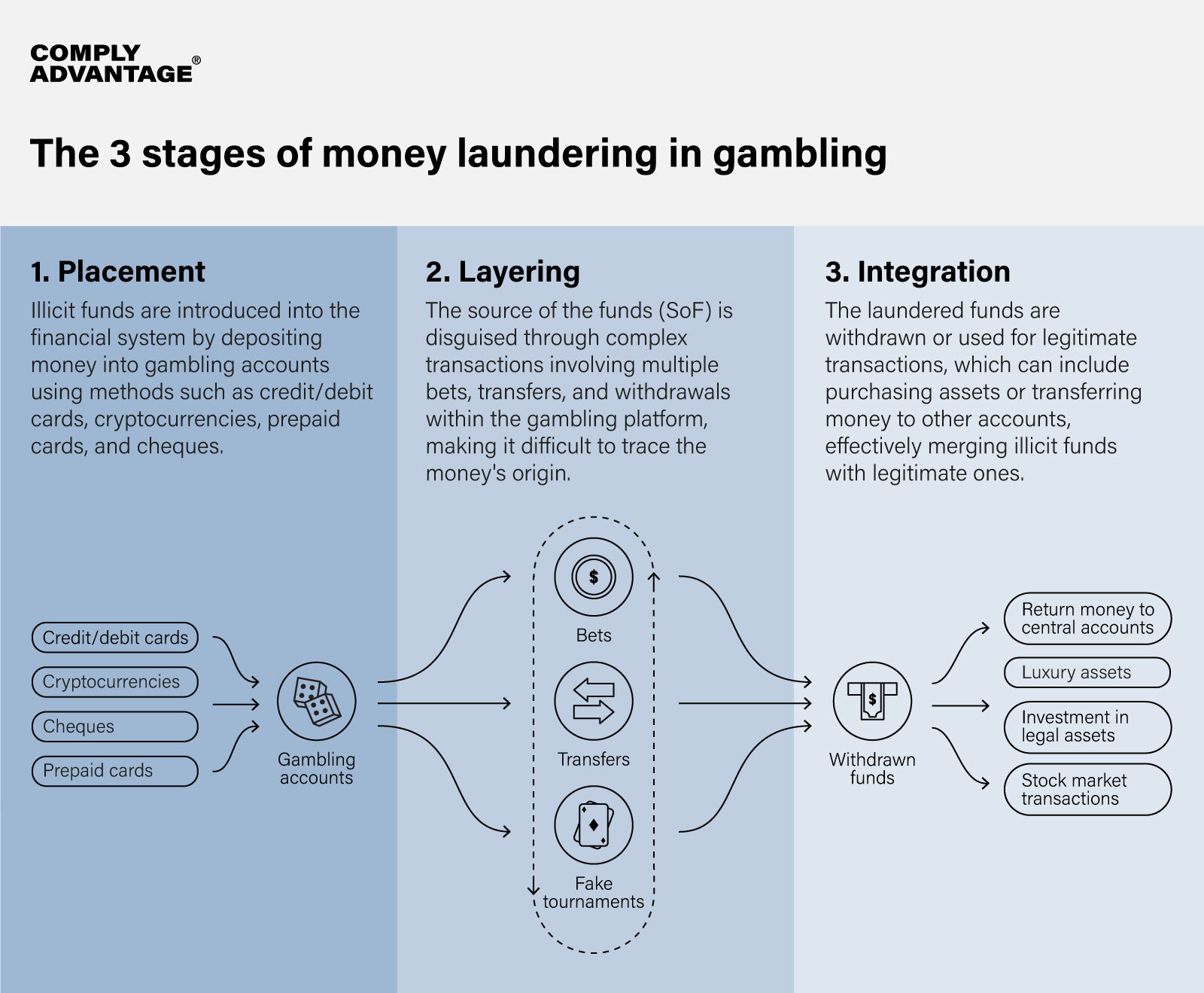
Understanding these stages can help identify some of the common schemes fraudsters use to launder money through online gambling platforms. Key methods to be aware of include:
- Smurfing: Breaking down large sums into smaller, less noticeable transactions to evade detection.
- Coordinated betting: Placing bets with deposited funds, colluding with other players, and making coordinated bets to obscure the money’s origin.
- Chip dumping: Intentionally losing chips to another player at an online poker table to transfer funds covertly.
- Player-to-player transfers: Using gambling accounts to facilitate illegal transactions between parties through direct transfers.
- Gnoming: Utilizing multiple accounts to help one player win and another lose in head-to-head games.
- Concealment: Hiding illicit funds in gambling accounts without immediate withdrawal, using the same anonymous banking method for future retrieval.
AML regulations for online gambling
In the US, online gambling falls under federal and state jurisdiction, with laws like the Wire Act governing interstate betting and payment processing. However, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) does expect online casinos to have the same robust Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and AML programs as traditional brick-and-mortar casinos. In fact, in June 2021, FinCEN issued its first government-wide priorities for AML and countering the financing of terrorism (CFT) policy pursuant to Section 5318(h)(4)(A) of the BSA. The regulator’s new policy identified eight national priorities for all bank and non-bank FIs covered by the BSA, including online gambling establishments, that must be incorporated into existing BSA/AML programs. The eight priorities include:
- Corruption
- Cybercrime
- Foreign and domestic terrorist financing
- Fraud
- Transnational criminal organization activity
- Drug trafficking organization activity
- Human trafficking and human smuggling
- Proliferation financing
Meanwhile, the EU lacks unified gambling legislation, with member states like France, Italy, and Spain each governing their regulations at the national level. These entities enforce licensing, consumer protection, and anti-fraud measures.
In the UK, the Gambling Commission oversees online gambling regulation, ensuring compliance with laws like the Gambling Act 2005. Specifically, all operators must comply with the following:
Penalties for non-compliance
The UK’s Gambling Commission has the authority to issue fines for breaches of the Gambling Act 2005. These fines can range from a percentage of annual revenue to substantial fixed penalties, depending on the severity of the violation – non-compliant operators may face license suspension or cancellation.
Similarly, in the EU, member states enforce penalties for non-compliance with gambling regulations. For example, under France’s Autorité de Régulation des Jeux En Ligne (ARJEL), operators can face fines of up to €30,000 for violating licensing conditions or regulatory requirements. Repeated offenses may lead to higher fines or even license suspension or cancellation.
In the USA, penalties for failing to comply with online gambling regulations vary at both the federal and state levels. Under the Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act (UIGEA), FIs can face civil penalties for processing illegal gambling transactions, with fines reaching up to $1 million per violation. Operators may also face prosecution under state-specific laws, such as New Jersey’s Casino Control Act, which imposes fines of up to $200,000 for each regulatory violation. Regarding BSA violations, the US government imposes statutory penalties – which can range from $10,000 dollars for record-keeping violations to over $200,000 for more serious infractions.
Money laundering red flags in online gambling
By recognizing financial red flag indicators about online gambling money laundering, firms can develop and implement specific rule sets and monitoring systems to identify and mitigate risks, ensuring they do not inadvertently facilitate illegal activities. Some of the most common indicators of potential money laundering in online gambling include:
- Unusual betting patterns: Players who consistently place large bets on low-risk games or matches may be attempting to launder funds by minimizing the risk of loss.
- Frequent and large transactions: Individuals making numerous substantial deposits or withdrawals within a short time frame could be moving illicit money through the platform.
- Funds originating from crypto: Gaming deposits originating from cryptocurrency, due to their pseudo-anonymous nature, can raise a red flag for potential money laundering. In February 2024, the UK Gambling Commission reminded operators that crypto-assets are considered high-risk, and licensees must appropriately scrutinize crypto transactions throughout customer and business relationships.
- Quick turnover: Depositing significant amounts and withdrawing them shortly afterward, without much gameplay, indicates an attempt to obscure the money’s origin.
- Multiple accounts and identities: Operating multiple accounts under different names or using various IP addresses can signify efforts to evade detection or circumvent transaction monitoring.
- Inconsistent behavior: Erratic gaming patterns that do not match deposit and withdrawal behaviors suggest the platform is being used as a conduit for illicit activity rather than for entertainment.
How can online gaming platforms mitigate money laundering risks?
While there are many risks associated with online gambling, FIs can bolster their defenses with the right application of diligence, software, and training. Outlined below are some best practices businesses should consider:
- Risk assessments: Ensure risk assessments align with the latest red flag indicators. This should include evaluating the risks associated with specific products and services, taking into account the user and the product’s functionality.
- Blockchain technology: Blockchain technology offers online gambling companies a transparent way to record transactions, providing an immutable ledger that can be audited for suspicious activities.
- Staff training: Comprehensive staff training on AML procedures and regulations is critical for ensuring compliance and fostering a culture of vigilance within any organization. Regulations in 21 US jurisdictions mandate that online gaming operators must prepare and submit a plan for addressing responsible gaming issues, which must include employee training and public awareness efforts.
Detect money laundering with advanced AML solutions
Advanced AML solutions employ a mix of sophisticated techniques to help compliance teams effectively monitor and prevent illicit financial activities. At the core of these strategies is transaction monitoring, which scrutinizes financial transactions to spot suspicious activities. Utilizing cutting-edge machine learning algorithms, these systems can identify irregular patterns like significant transfers to offshore accounts, recurring high-value transactions, or movements inconsistent with a customer’s usual profile, triggering alerts for further investigation.
Customer screening is also vital as it aims to verify the identities of both new and existing customers against databases of known criminals, politically exposed persons (PEPs), and sanctioned individuals. This step is crucial for preventing high-risk individuals from using online gaming platforms for money laundering, helping firms mitigate the risk of non-compliance and protect their reputations in the market.
 Mon - Fri ( 9:00 am - 5:00 pm )
Mon - Fri ( 9:00 am - 5:00 pm )  +971 52 5200 232
+971 52 5200 232  hello@consiliumadvisory.me
hello@consiliumadvisory.me  https://www.linkedin.com/company/consilium-advisory/mycompany/?viewAsMember=true
https://www.linkedin.com/company/consilium-advisory/mycompany/?viewAsMember=true 